
May 23, 2024
TABLE OF CONTENTS

A search-engine-friendly website means that it is easier for search engines to crawl and to index.
Crawl – find, update, and download info from web pages
Index – analyze text, images, & videos and store them
To begin creating your SEF website, choose a hosting provider such as Bluehost, choose a Content Management System (CMS) such as WordPress.org, and integrate the Elementor Pro and Yoast SEO plugins.
Elementor is “the #1 website platform for WordPress“
Not only are keywords search engine friendly and user friendly, they make your site more accessible for people with disabilities. According to WebAIM – WebAIM (Web Accessibility In Mind) who has been providing comprehensive web accessibility solutions since 1999 – “… headings are the primary mechanism used by screen-reader users to navigate content…”
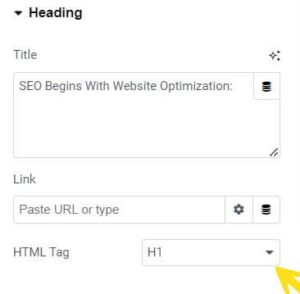
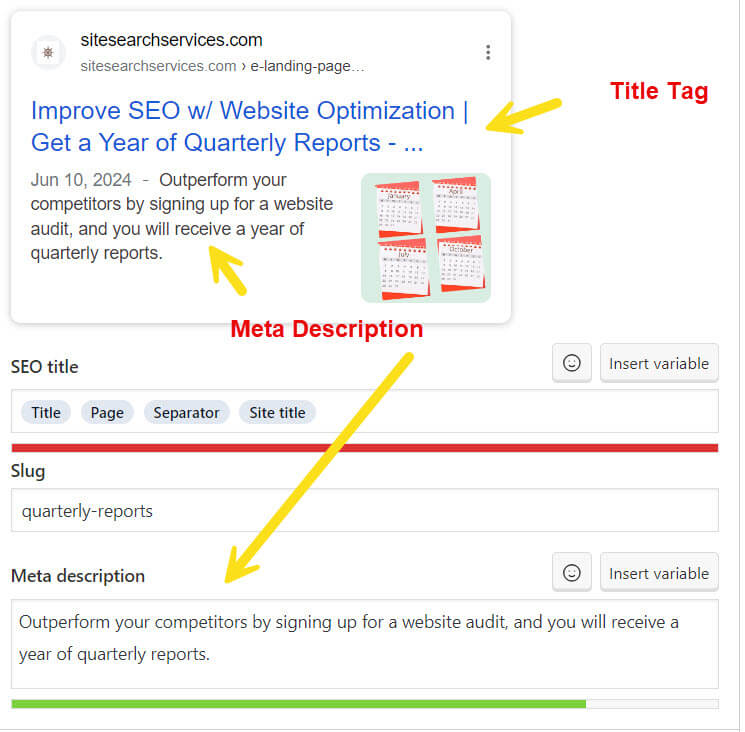

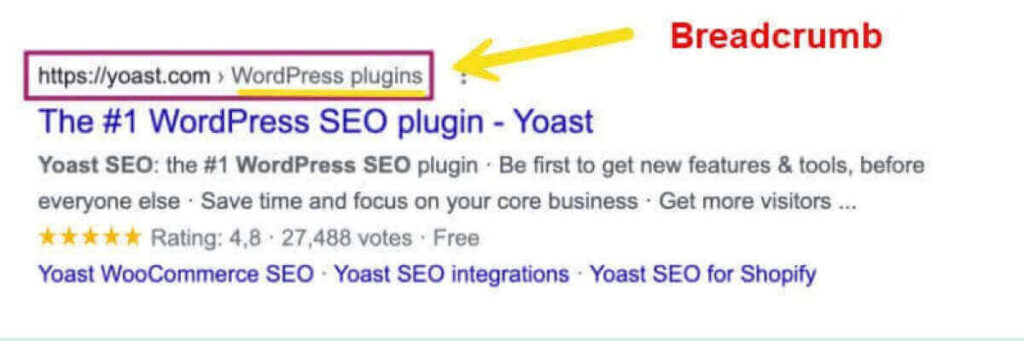
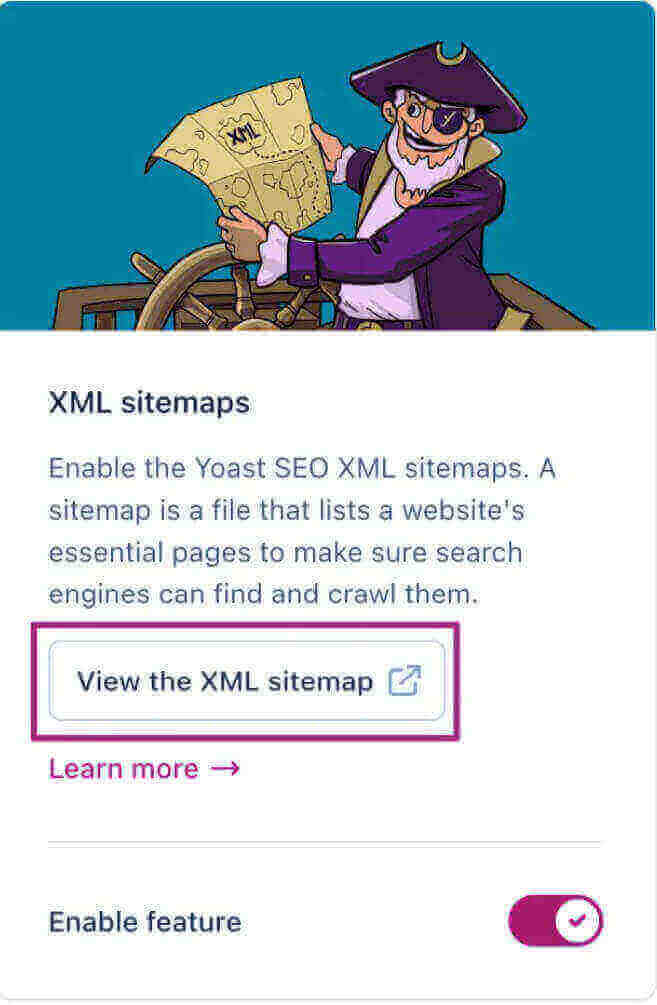
HTML, XML, and IMAGE
“If you feel the need for an HTML sitemap, you should spend the time improving your site’s architecture instead.”
Disclaimer – Last Updated 08-30-2024
To protect consumers’ interests, businesses are required by the FTC to present a disclosure proclamation for businesses we are affiliated with and from whom we receive monetary compensation.